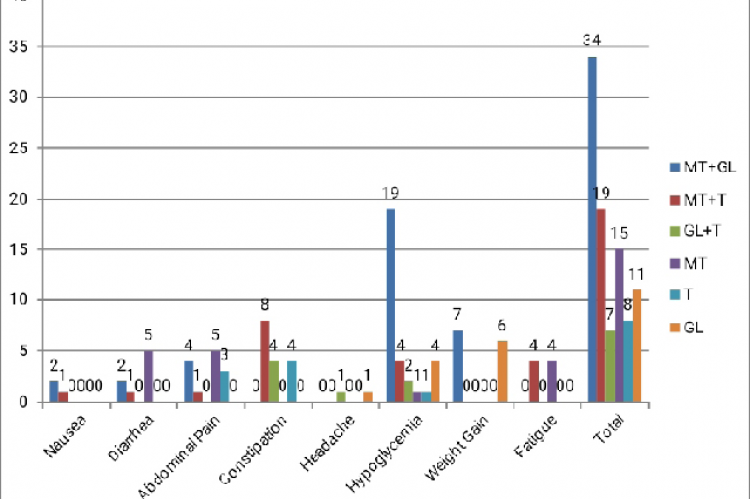
Aims: The purpose of the study was to determine the safety and efficacy of Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4-Inhibitor as mono-therapy and in combination therapy. The impact of age, disease duration and gender on the efficacy of DPP-4 inhibitors were also studied. Materials and Methods: A prospective observational study was conducted among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. The study consisted of 6 groups: Metformin+Glimepiride, Metformin+Teneligliptin, Glimepiride+Teneligliptin, Metformin only, Teneligliptin only and Glimepiride only. Fasting and Post Prandial Blood Sugar and HbA1c were monitored before and after 6 months of therapy. Results: In combination therapy, the adverse effects were higher in Glimepiride and Teneligliptin group followed by Metformin and Glimepiride and Metformin and Teneligliptin. The mean FBS reduction was 21.57 mg/dl, 28.32 mg/dl, and 20.08mg/dl in Metformin+Glimepiride, Metformin+Teneligliptin and Glimepiride+Teneligliptin, respectively. The mean Post-Prandial Blood Sugar reduction was 27.63mg/dl, 42.78mg/dl, 34.13mg/dl in Metformin+Glimepiride, Metformin+Teneligliptin and Glimepiride+Teneligliptin, respectively. The mean HbA1c reduction was 1.30%, 1.41%, and 0.80% in Metformin+Glimepiride, Metformin+Teneligliptin and Glimepiride+Teneligliptin, respectively. Conclusion: Metformin and Teneligliptin combination therapy and Teneligliptin monotherapy were safe and efficacious compared to all other oral hypoglycemic drugs under study. There was no significant impact of gender, BMI class and disease duration on the drug’s efficacy.
View:
- PDF (2.68 MB)